A traditional acoustic piano can play the notes you see on the keyboard. All pianos have a sustain pedal that can keep notes sounding, after you release the keys. Many pianos also have a "soft" pedal that can mute the volume and a sustenuto pedal that sustains selected notes.
But when digital pianos were invented, it became possible to expand the functionality of the piano. In this article, we will go over some of the most common functions, features, and effects found in modern digital pianos. These functions can be very practical as they can help you learn to play more effectively.
Basic functions
- Voice select
- Metronome
- Record/play
- Transpose
- Tuning
- Polyphony
Extra functions
- Split-function
- Dual-function
- Equalizer
- Reverb
- Touch sensitivity
- Bluetooth MIDI/AUDIO
Voice select
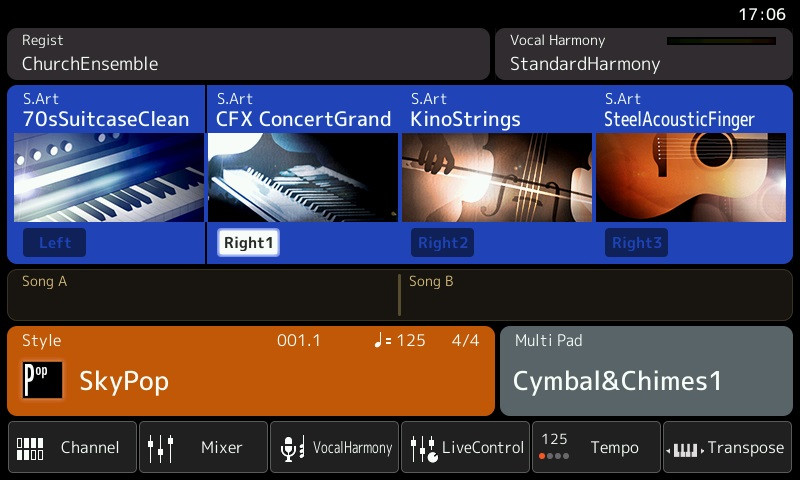
A feature found in all digital pianos is the ability to switch between different sounds. Some keyboards and synthesizers have many different kinds of sounds, such as bells, percussion, mellotron or even animal sounds. Digital pianos (as opposed to keyboards) often do not have as many different types of sounds, but instead, a larger selection of piano sounds and sounds from other keyboard instruments, such as e-piano, harpsichord and organ.
Metronome
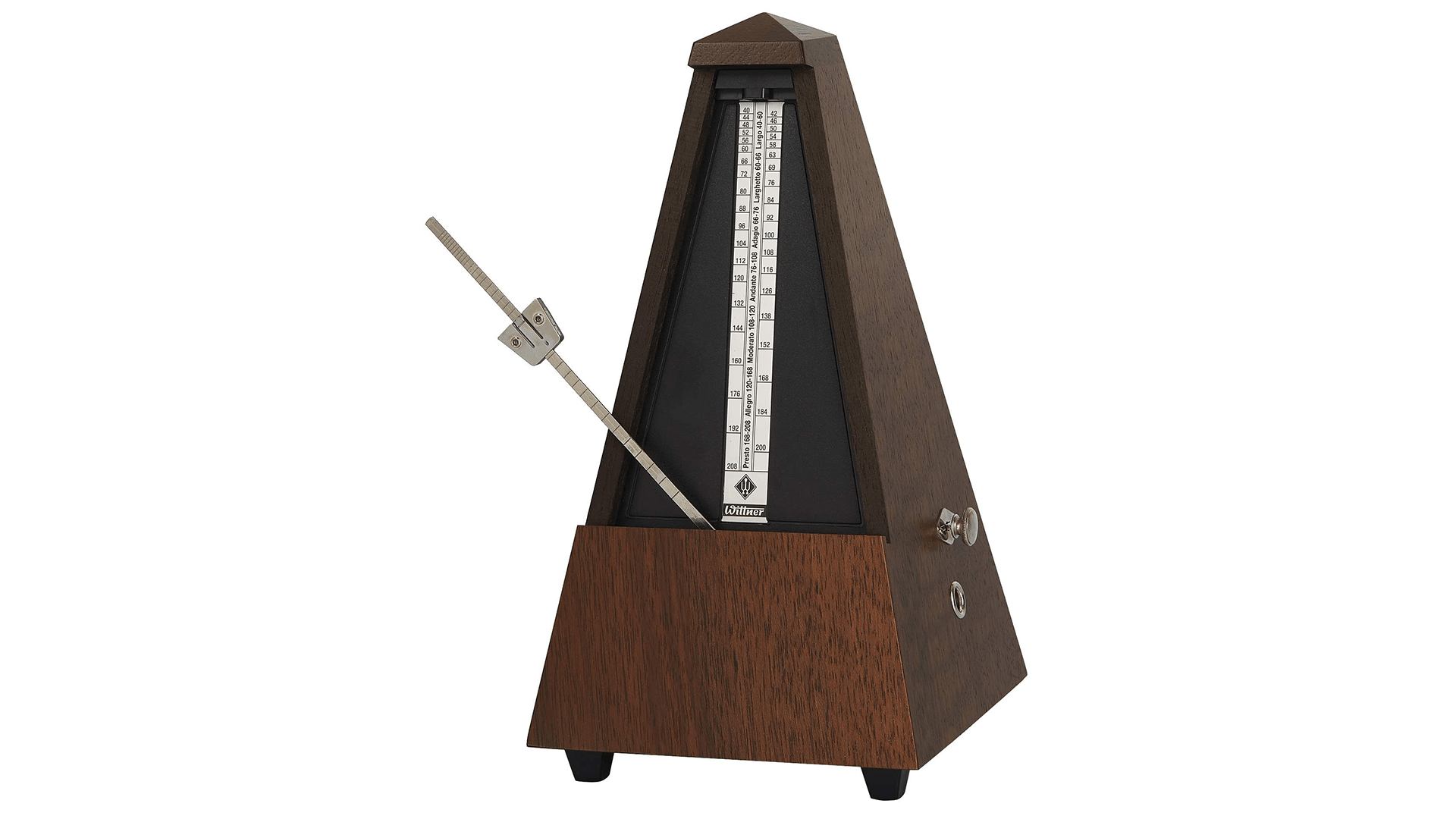

A metronome helps you keep pace. You specify a tempo, which is subsequently played with clicks from the instrument. The tempo is in beats per minute, and can be set to different beats, and whether you want to hear a one-beat or not. A metronome is good to have for rehearsing a piece of music at a certain tempo and technical practice. Built-in metronomes are found in almost all digital pianos.
Record/play
A built-in recorder is useful in several practice situations. Apart from the fact that it can be fun to hear yourself play, it is also practical to be able to refine your playing from what you hear or save creative musical ideas for later. On many instruments, you can record on several tracks. If this is not enough, you can also connect most digital pianos to a computer and use a recording program to record as many tracks as you want.
Transposing

The transpose function gives you the opportunity to transpose to another key. When you switch to another key, you change the pitch of the entire piece and thus get a completely different starting point. It can be useful in a situation where you have learned to play a song, where the melody starts on C, for example, but you need to play it starting on F. This is especially useful if you are accompanying vocalists who want to sing in a higher or lower key.
Tuning

You may have heard that guitars or acoustic pianos can "go out of tune". This means that the strings in the instrument are not adjusted to the standard. The A440 is the musical pitch, corresponding to a sound frequency of 440 Hz, which acts as a tuning standard for the musical tone "A" over the middle C (also called A₄ in scientific pitch notation). A digital instrument, on the other hand, cannot go out of tune - there are no strings to tune. However, it is still possible to tune it, if you wish.
In some instances, some songs or pieces are written in a special tuning, and you may therefore need to tune your piano a little up or down to be able to play along with other musicians.
Polyphony

Polyphony is not a function, per se, but rather a concept that is good to know about, when searching for a digital piano. For most regular pianists, a polyphony of 128 is just fine. The highest polyphony on the market is 256 or Roland's "limitless". Polyphony is an expression of memory of the number of tones that can sound simultaneously. If you imagine that you will need to play then sustain a large number of notes simultaneously, which is common in advanced piano music, then it is good to have as much polyphony as possible.
Split function
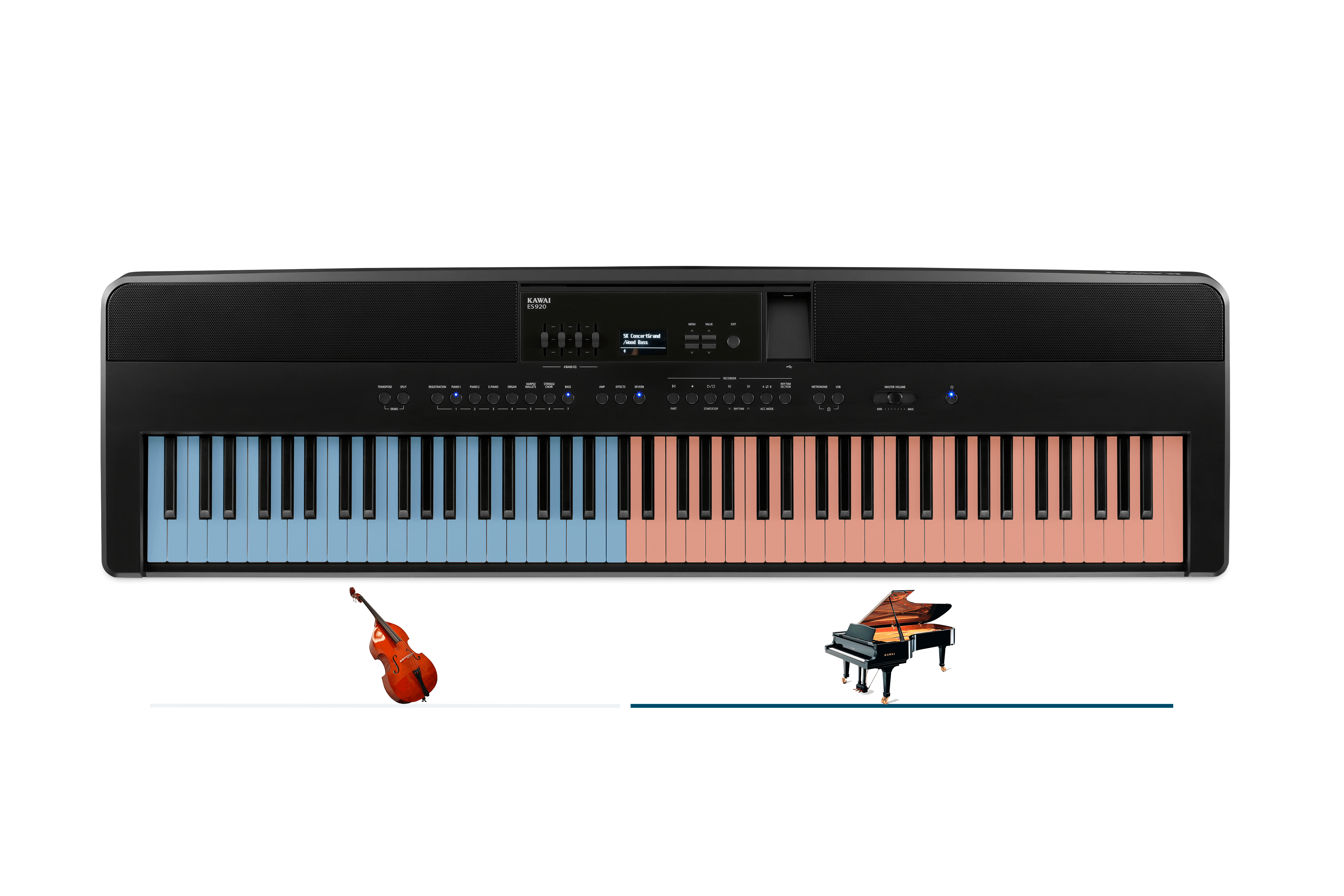
The split feature lets you play different sounds on the piano, at the same time. You "split" the piano, so you e.g., have a bass sound in the lower part of the keyboard, and a piano sound in the upper part. You can also combine strings, winds, choir singers, synth sounds or anything else - only the imagination sets limits. On some instruments, you can choose where you want to divide the piano (your "split-point"). Some of the more advanced instruments can have 3 or 4 split points and play many different sounds at the same time.
Dual function
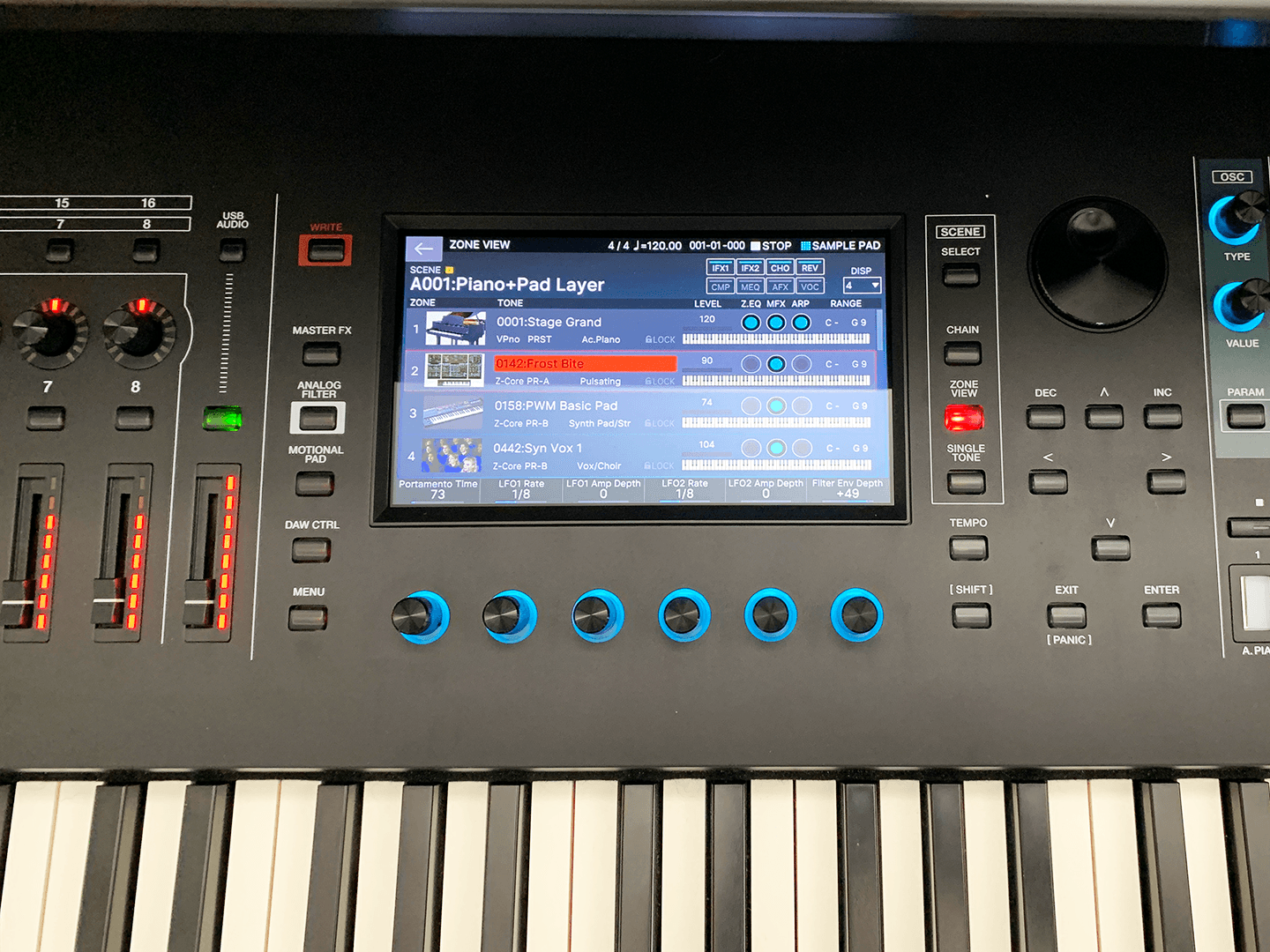
The dual (or layer) function is similar to the split function. Here you can also select 2 (or more) sounds that you play at the same time, but instead of splitting the sounds separately, they are layered on top of each other. With these kinds of features, you can really expand your soundscape, so that when you're playing alone, your music sounds as if it was played by an entire orchestra. Many pianos with dual function also have the option to adjust the volume of the different sounds, individually.
Equalizer
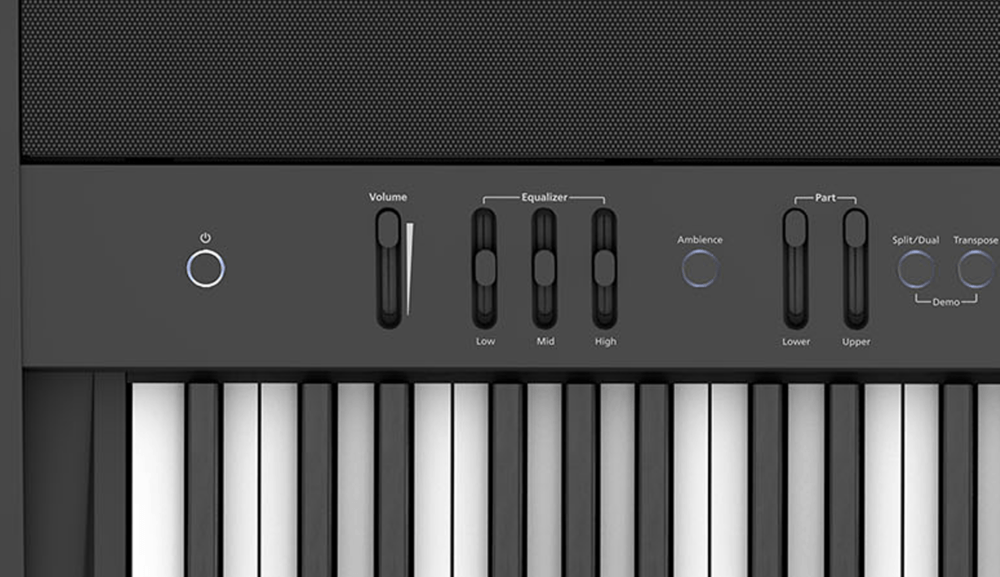

An equalizer is a sound engineering tool whose primary task is to adjust the various frequency ranges. An equalizer can raise and lower the volume in selected areas of the sound spectrum, giving the overall sound picture a different balance. You usually divide your EQ into three: Low (bass), mid and high (treble). This is one of many ways in which you can fine-tune and personalize your sound.
Reverb

Reverb is the persistence of sound after it is produced. Reverb is created when a sound is reflected off, of a surface causing numerous reflections to build up. Reverb defines how a sound is reflected in any given space. Many digital pianos have a function that mimics different kinds of reverberations, from a small room to a stage or to a concert hall.
Touch-sensitivity
Dynamics are an essential part of musical expression. It is not possible to change the actual “feel” of the keys in a piano, since it is purely mechanical.
With digital pianos, however, you can often adjust the sensitivity of the keyboard sensors. This way, you can choose between a more or less dynamic spectrum, for your piano playing. If you play music in e.g., baroque style, it can be good to have a fairly even and balanced dynamic range. If, on the other hand, you play Romantic repertoire, it's often better with powerful fortissimo and subdued pianissimo.
Bluetooth MIDI/AUDIO

When talking about digital keyboards, Bluetooth can be divided into two functions: MIDI and AUDIO.
With Bluetooth MIDI you can e.g. record directly into Garageband, write notes directly in a sheet music program, or use a professional program to change MIDI settings. Some digital pianos today also use the Bluetooth functionality to connect to an App that the various manufacturers have developed, e.g., Roland's app, "Piano Partner 2" or Yamaha's "Smart Pianist".
With Bluetooth AUDIO connection, you can connect your "smart device" to the piano wirelessly, and the idea is that you can play sound through the speakers on the instrument. So, if you have a favorite song, it can be played via. the speaker system of your instrument. You can even play at the same time, so the speakers play both the song and your piano playing.